ZERO CITIES PROJECT
ZERO CITIES PROJECT DATA & ANALYSIS
Building stock assessments, conducted for all Zero Cities, compiled city-wide and sub-sector building area, size, energy consumption, fuel types, and greenhouse gas emissions data. Future projections of the assessments were also estimated. The intents of the assessments were to:
- inform and direct future Zero Cities project work,
- create a method for analyzing the likely carbon and energy impacts of various policies and strategies, and
- create a set of common metrics for all Zero Cities.
Project assessments include:
Cities contain various building typologies that can be categorized by building floor area.
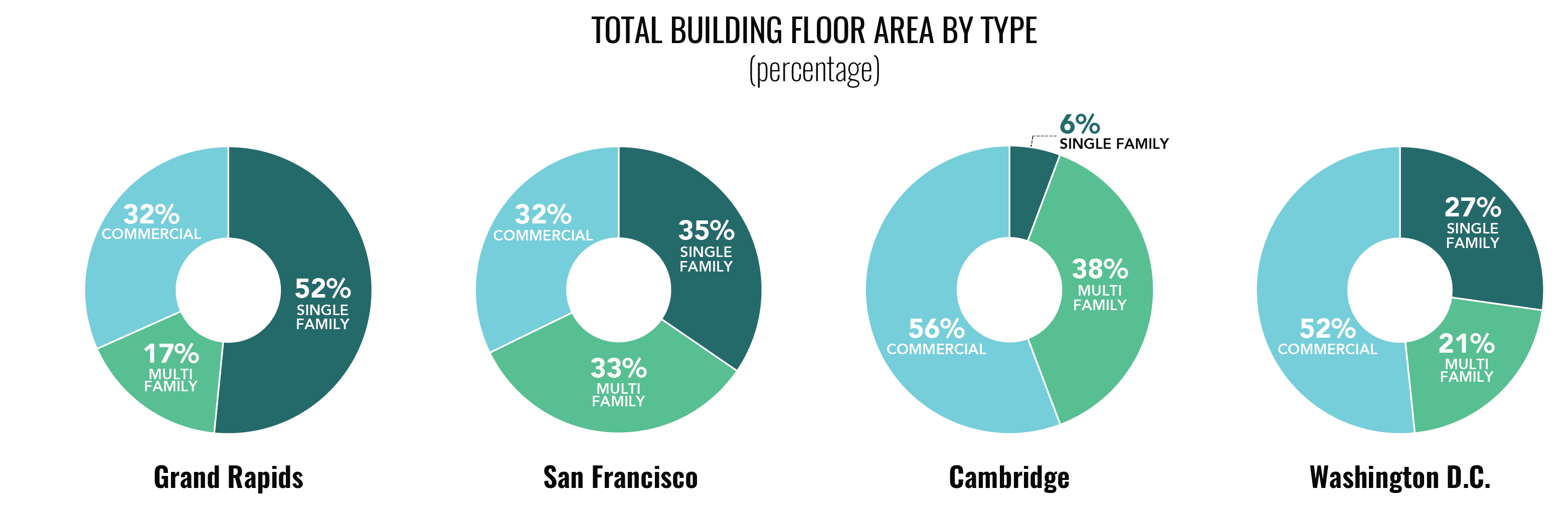
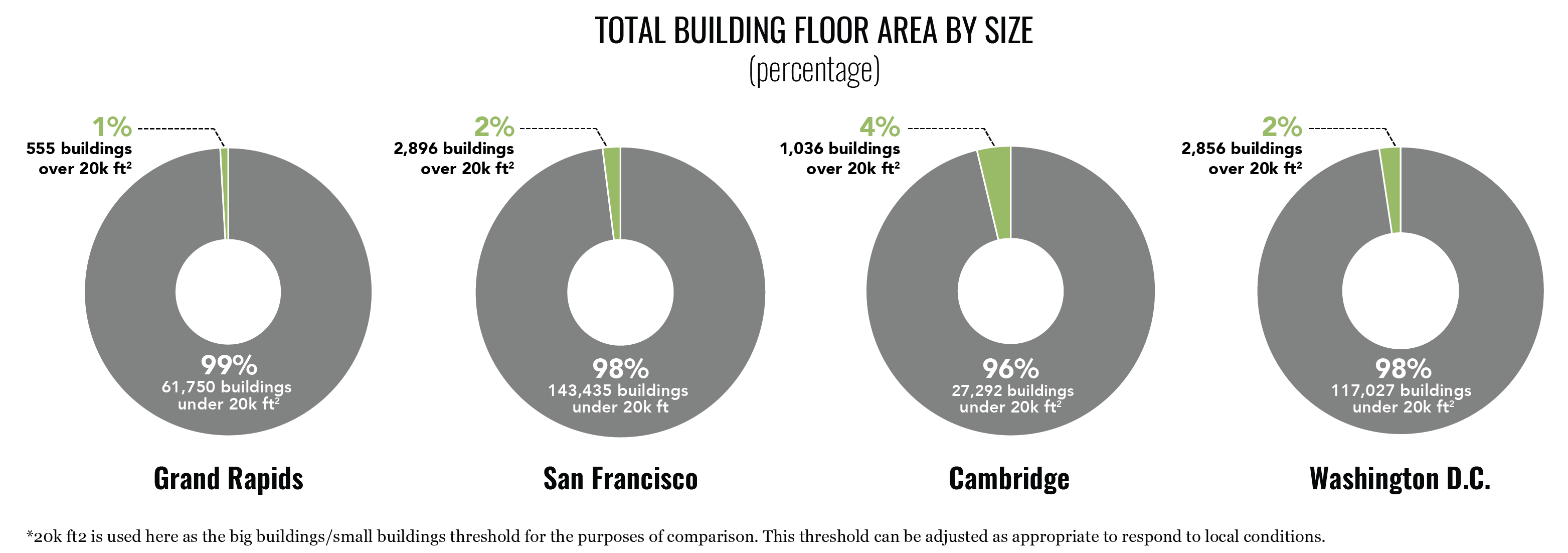
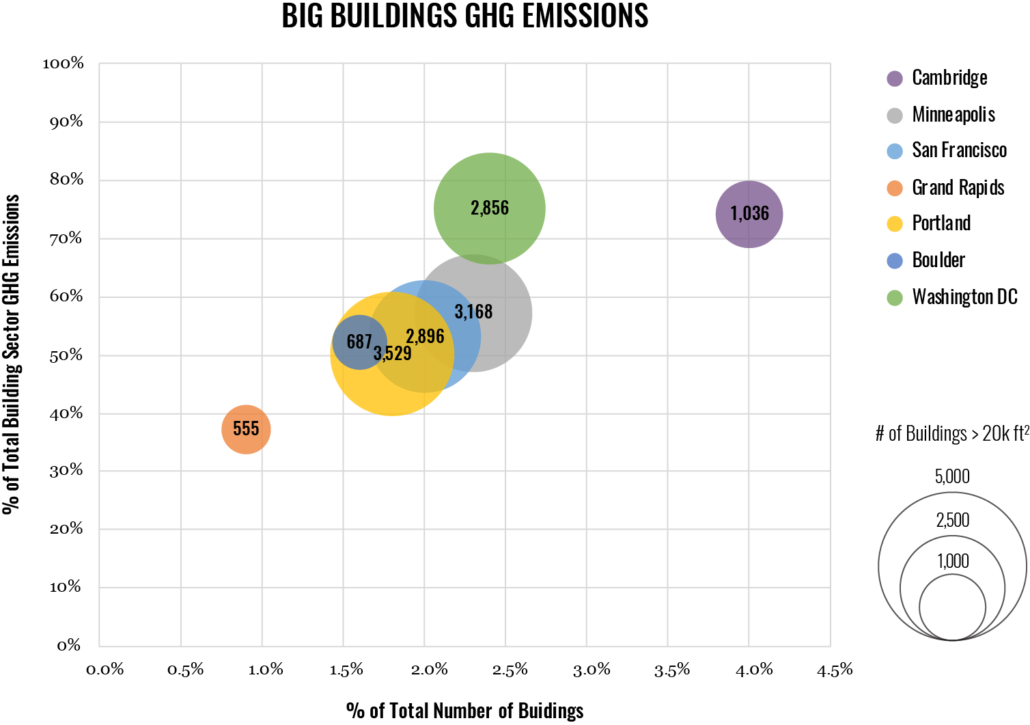
In most cities, there are relatively few BIG buildings and a large number of SMALL buildings*.
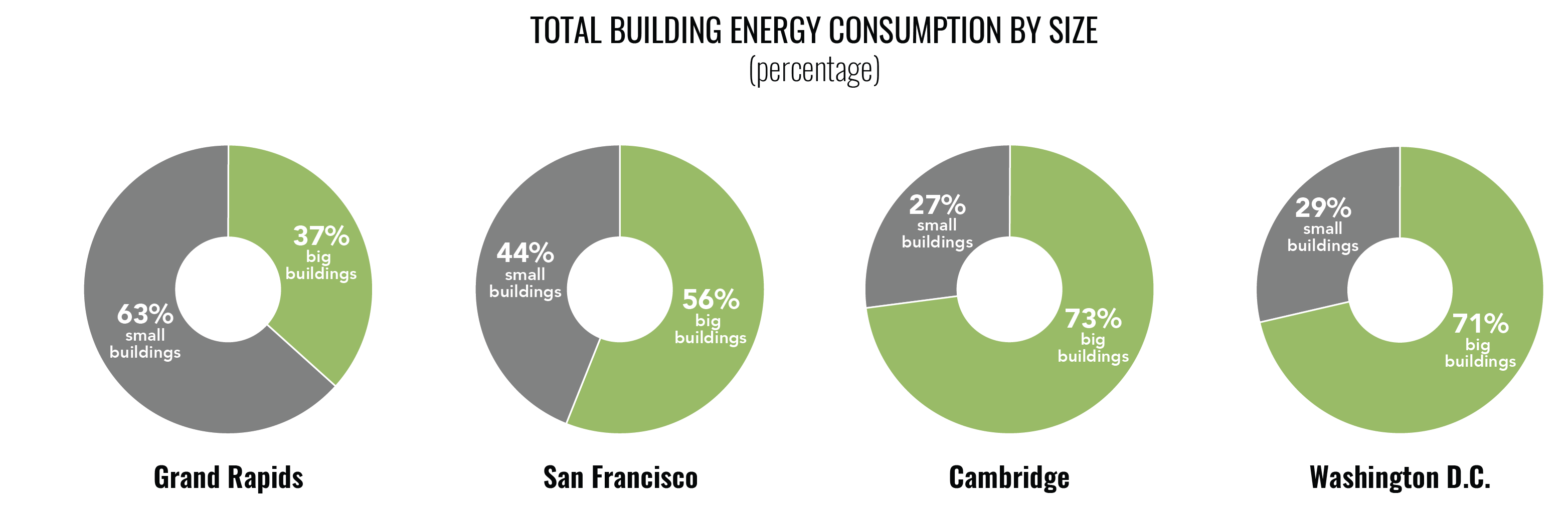
In cities, the few BIG buildings and many SMALL buildings are each responsible for a significant portion of city-wide building sector energy consumption.
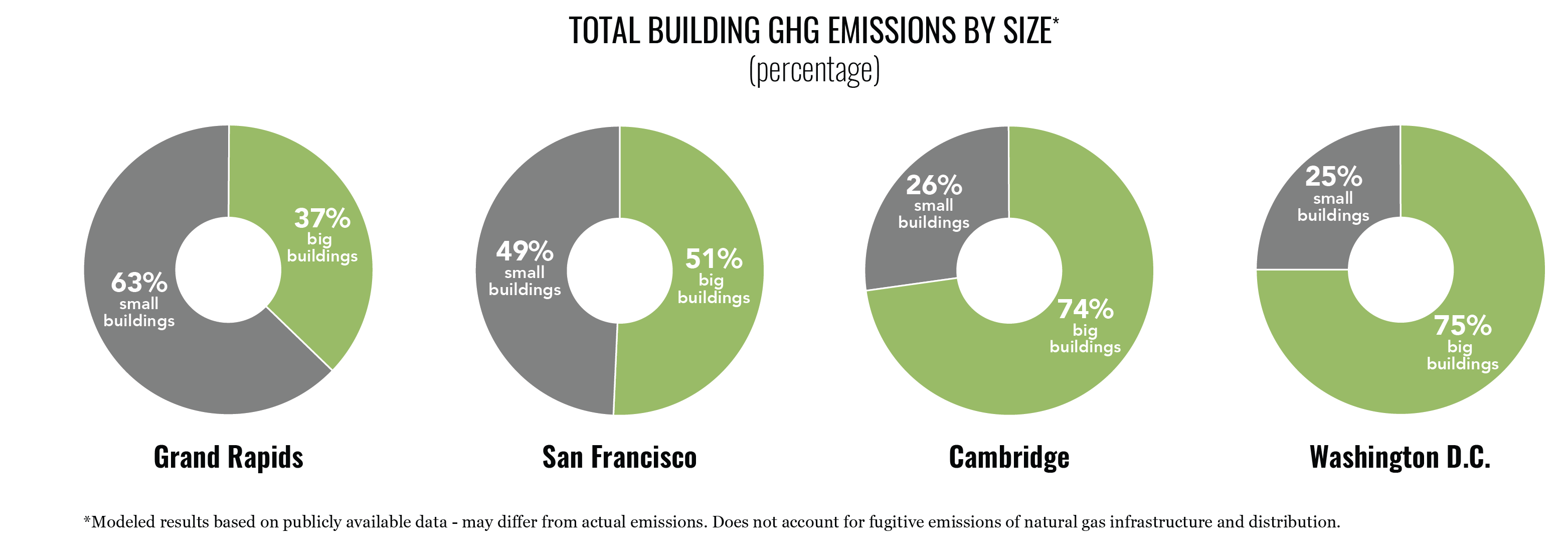
In cities, the few BIG buildings and many SMALL buildings are each responsible for a significant portion of city-wide building sector GHG emissions.
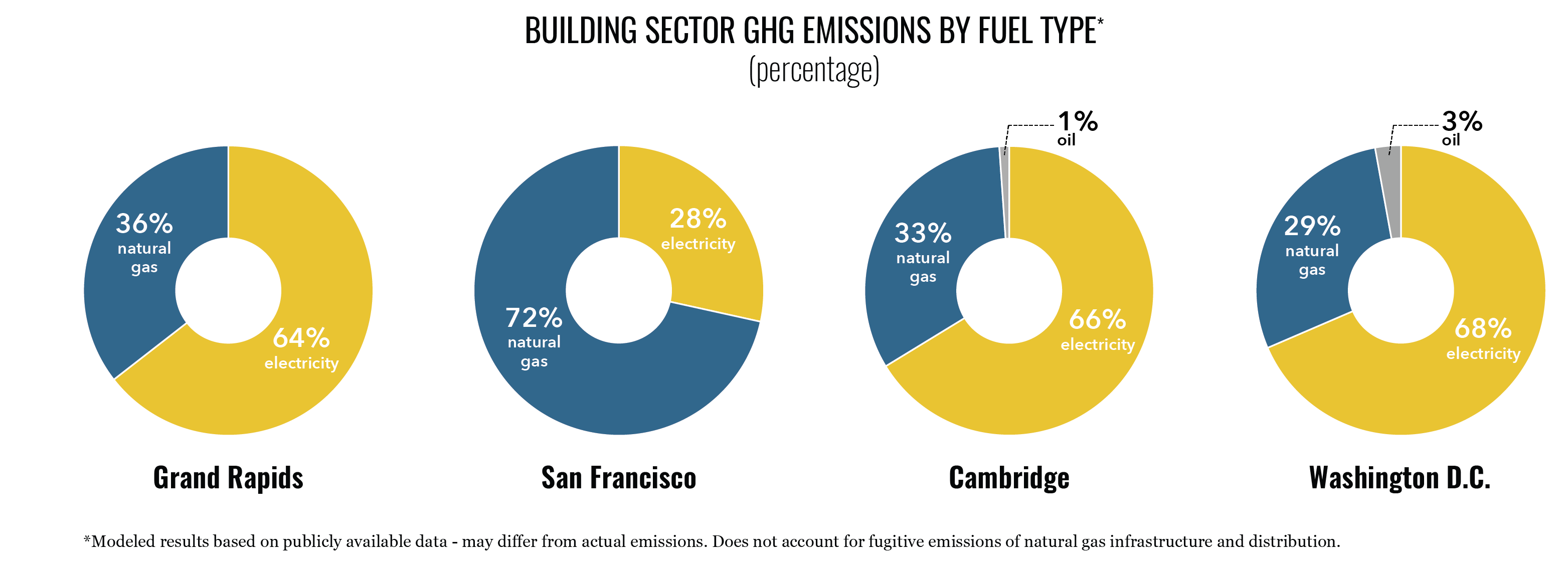
The fuels used to meet building sector energy needs vary by building typology and climate. However, most buildings use a significant amount of electricity and on-site natural gas.

A variety of fuels are used by utilities to generate electricity. The emissions associated with each fuel, frequency of fuel use, and the efficiency of a power plant all contribute to the emissions intensity of the electricity supply.
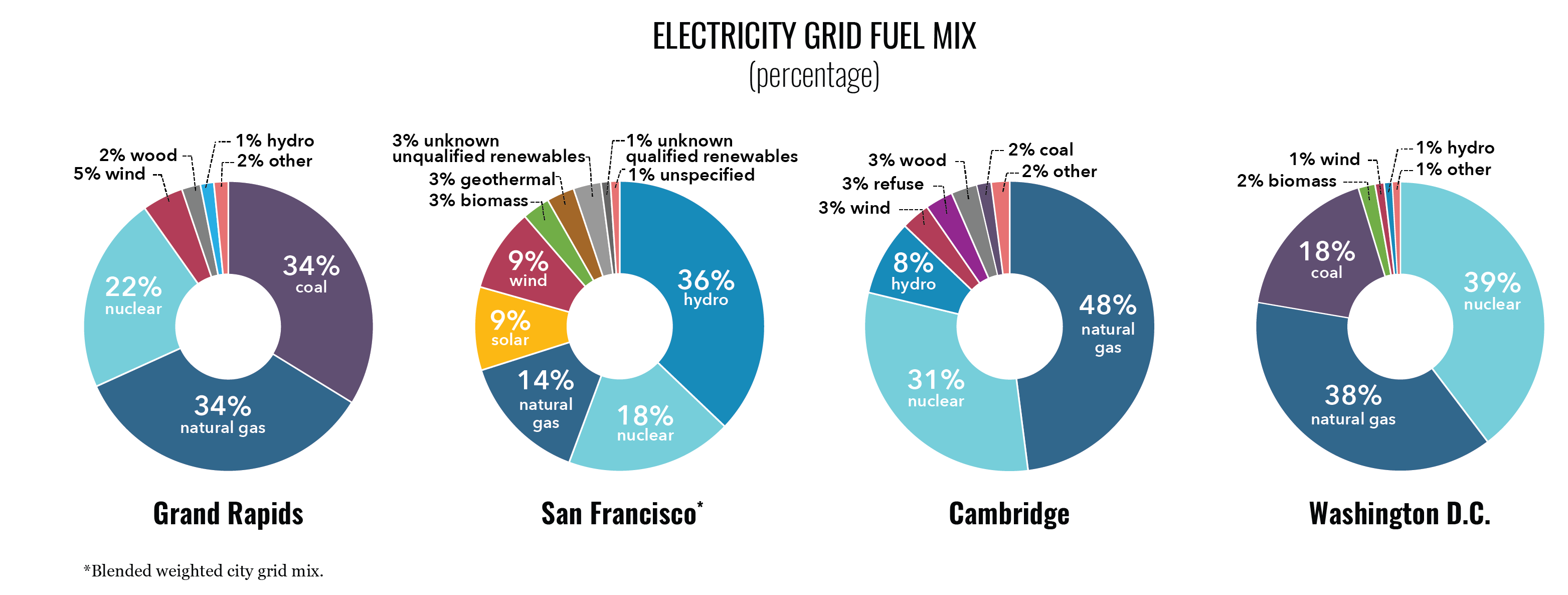
Each fuel’s proportion of city-wide building sector emissions can vary dramatically due to the emissions intensity of the electricity supply and on-site fuels.
In all cities studied, a small number of buildings (0.5-4.0% of buildings) represent a large percentage of total building floor area and energy consumption (35%-75% of energy consumption).

The emissions intensity of the electricity grid varies significantly by city.
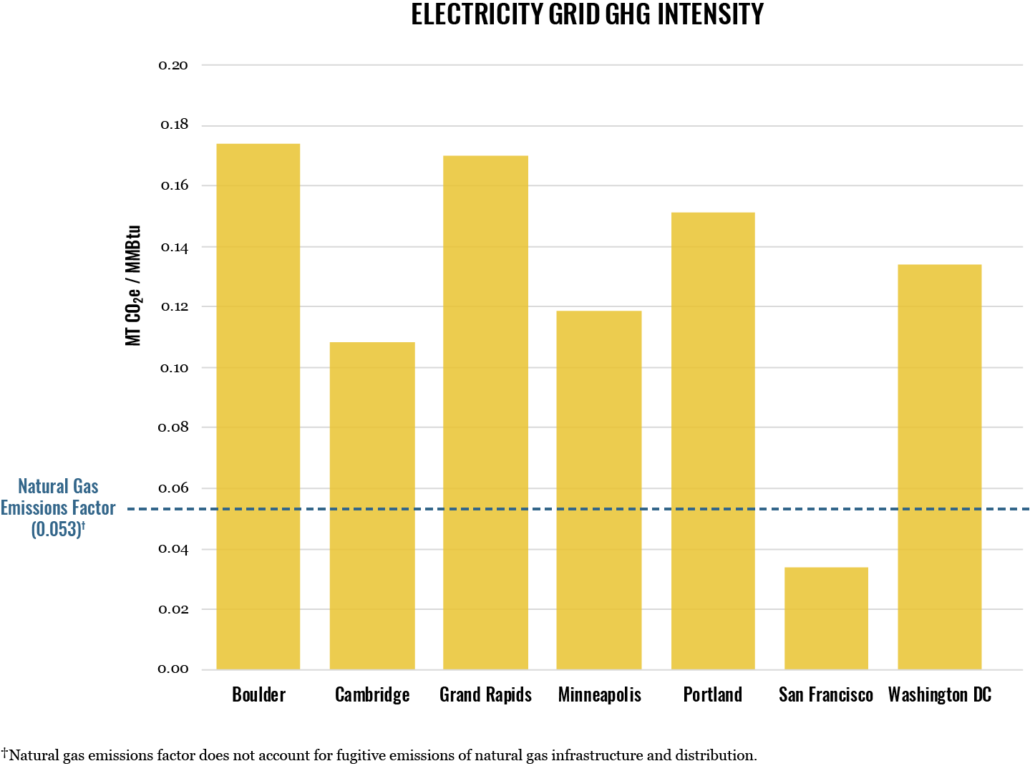
In all cities studied, a small number of buildings (0.5-4.0%) are responsible for a large percentage of total building sector emissions (35-75% of emissions). Variations between cities depend largely on the emissions intensity of the electricity grid.
Achieving Zero
Reaching a 50-65% carbon emissions reduction in the built environment by 2030, and zero emissions by 2040, is critical if we are to successfully manage climate change. Achieving Zero is a framework and set of tools to help city and sub-national governments (state, provincial, and regional) meet this target.
Contact
Architecture 2030
+1 (206) 438-3456
info@achieving-zero.org

